About
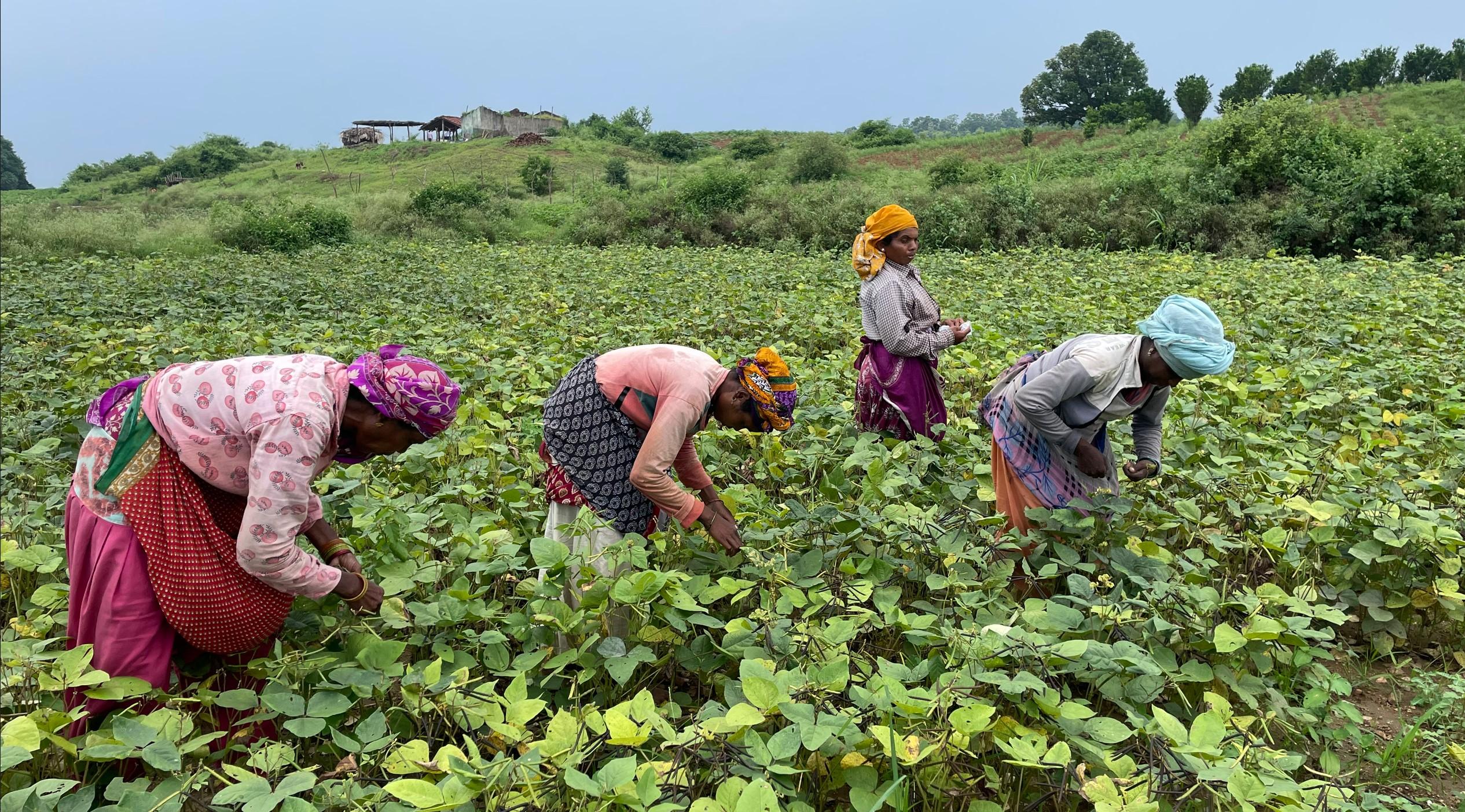
Western Madhya Pradesh can be classified into three agro-climatic zones (ACZs) i.e., Jhabua Hills, Nimar Plateau, and the Malwa Plateau. This region is marked by concentration of tribal households. According to Niti Aayog’s Multi-dimensional Poverty Index (MPI) report, districts such as Alirajpur and Jhabua are among the poorest districts of Madhya Pradesh. While agriculture is the primary income for households (~90%) in the region, major challenges exist for agricultural production systems in Western MP, which include:
§ Significant yield gaps across crops ranging from 50-100 percent.
§ Low organic carbon and poor nutrient (NPK) availability in the soil.
§ High chemical pesticides usage, poor water use efficiency and high GHG emissions due to intensive tillage and non-optimum fertilizer and water.
§ In addition, participation of women in decision making is very low in the region.
Founded by IDH, Laudes Foundation and WWF-India, RPLC is working in 8 districts of Western Madhya Pradesh with local partners on a Landscape approach. The approach aims to catalyse a transition towards a year-round and cross commodity engagement to build a business case for inclusion of smallholders in service delivery and sourcing via a self-sustaining ecosystem with the following key objectives:
§ Improving smallholder incomes towards a living income
§ Reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural and allied activities
§ Restoring and revitalizing soil health and soil carbon content
§ Improving access to and management of water as a resource
§ Preserving and enhancing biodiversity through nature-based solutions
§ Improving gender equity and empowerment of women